Classification of limestone
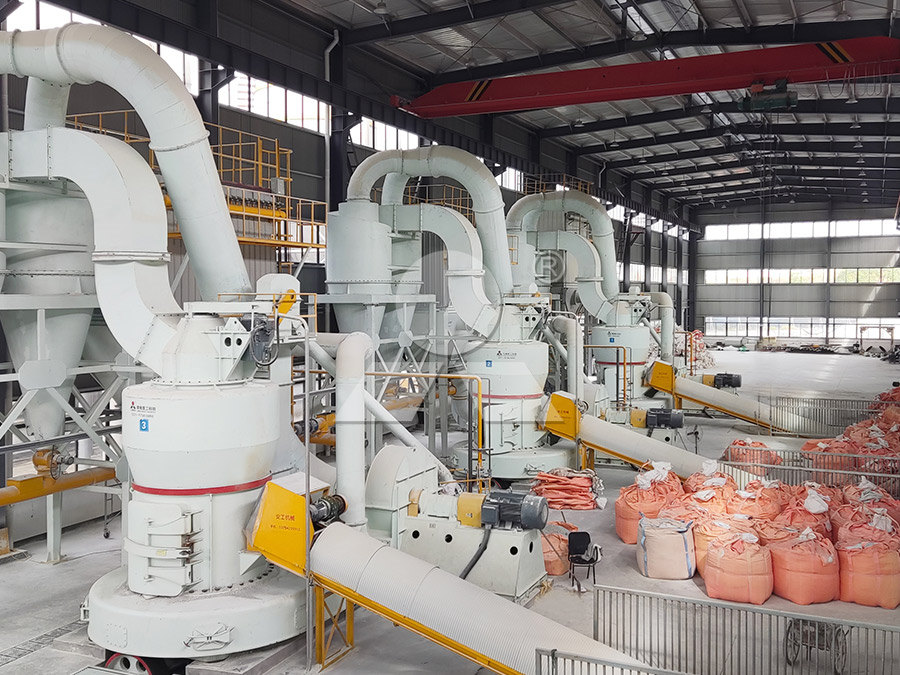
CFB石灰石脱硫剂制备——磨机公众号12.8 推送案例(8)51.jpg)
A revised classification of limestones ScienceDirect
1992年3月1日 The most widely used classifications of limestones are now thirty years old and our appreciation of the diagenetic effects on limestone textures is now much greater A 2023年12月19日 Folk's classification system is based on three basic components of limestone: Allochems (sediment grains): framework component of the rock There are four major types of allochems in Folk system: intraclasts, Carbonate sedimentary rocks classification AAPG WikiAll classifications of limestones are arbitrary and they frequently overlap or do not fit ones particular needs Since binocular microscopes or hand lenses are the tools that are commonly available to the explorationist, a practical Carbonate Classification SEPM Strata2024年1月7日 The classification of limestone is based on several factors, including its formation process, texture, and composition Two widely recognized classification systems, the Folk and the Dunham,Limestone: characteristics, formation, uses ZME Science

List of types of limestone Wikipedia
This article lists types of limestone arranged according to generic type and location Coquina from Florida This section is a list of generic types of limestone The following sections include both formal stratigraphic unit names and less 2018年2月2日 There are two main, complementary, classifications of limestone Both have advantages and disadvantages Folk’s classification (Folk 1959) describes the composition of Limestone SpringerLinkLimestone is a very common sedimentary rock consisting of calcium carbonate (more than 50%) It is the most common nonsiliciclastic (sandstone and shale are common siliciclastic rocks) sedimentary rockLimestones are rocks that Limestone Sedimentary rocks SandatlasTheir various sizes, from boulders to clay, is referred to as the sediment grain size The classification and description of the various clastic rocks appears in the top section of the chart below Crystalline limestone is a carbonate 55: Classification of Sedimentary Rocks Geosciences

Limestone Characteristics, Formation, Texture, Uses,
2024年10月30日 Limestone, sedimentary rock composed mainly of calcium carbonate, usually in the form of calcite or aragonite It may contain considerable amounts of magnesium carbonate (dolomite) as well; minor constituents also 2019年9月4日 A post in the How to series on carbonate mineralogy – limestone classification The classification of carbonate rocks, like that of sandstones, has gone through a few iterationsTwo schemes have stood the test of trial and error, in the field and through microscopes; both were compiled in the late 1950s – early 60s, each serves a slightly different The mineralogy of carbonates; classification Geological The most widely used descriptive classification to define the type of limestone found in field work is that of Dunham (1962) For the classification it is necessary to base it on the texture, structural characteristics, the relationships of the primary structural components: grains (intraclasts, granules, pelloids, wrapped grains, bioclasts and skeleton), carbonate mud and calcite cementLimestone: Properties, Characteristics and Uses GeossaryA triangular diagram showing the relative proportions of allochems, calcite ooze matrix, and sparry calcite cement is used to define three major limestone families Family I consists of abundant allochems cemented by sparry calcite; these are the cleanly washed limestones, analogous with well sorted, clayfree sandstones and similarly formed in loci of vigorous currentsPractical Petrographic Classification of Limestones1
.jpg)
Classification of Carbonates SpringerLink
Folk limestone classification table identifies the component (or allochemical) particles and whether the matrix is micrite or lime mud or a sparry calcite cement precipitated between the grainsShould intraclasts form >25% of the grains, then the rock is named an intraclastic limestone; if intraclasts are 25%, the rock is an oolitic limestone; if intraclasts and ooids are Download scientific diagram Folk classification of limestones based on textural parameters and implied depositional conditions from publication: Integrated Porosity Classification and Folk classification of limestones based on textural parameters and 1992年3月1日 The most widely used classifications of limestones are now thirty years old and our appreciation of the diagenetic effects on limestone textures is now much greater A revision of the classifications of Dunham (1962) and Embry and Klovan (1971) is offered and new “diagenetic” categories are proposedA revised classification of limestones ScienceDirectWhat is Limestone? Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed primarily of calcite, a calcium carbonate mineral with a chemical composition of CaCO 3It usually forms in clear, calm, warm, shallow marine waters Limestone is usually a biological sedimentary rock, forming from the accumulation of shell, coral, algal, fecal, and other organic debrisLimestone: Rock Uses, Formation, Composition, Pictures
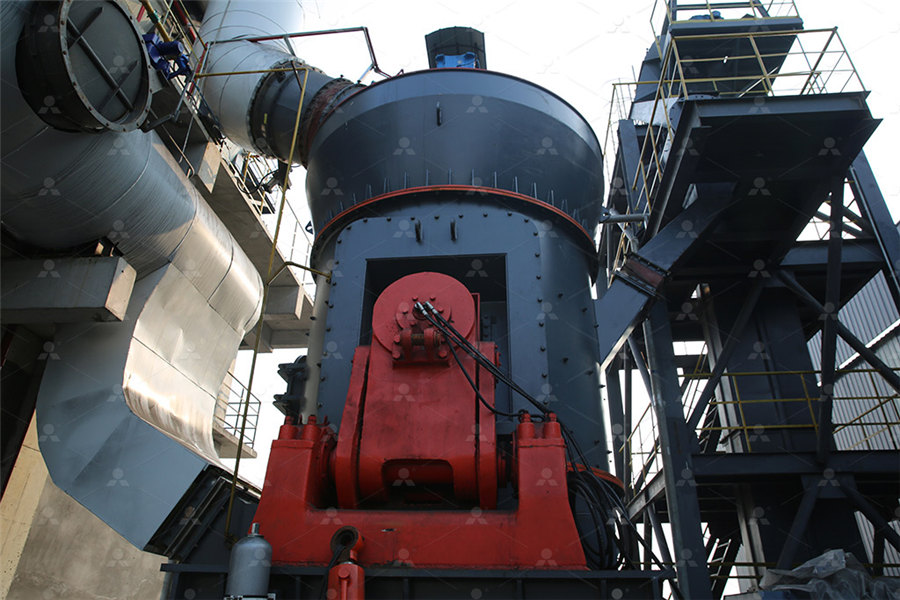

Limestone PPT Free Download SlideShare
2012年5月21日 16 USES OF LIMESTONE It can suppress methane explosions in underground coal mines Purified, it is added to bread and cereals as a source of calcium Calcium levels in livestock feed are supplemented with it, such as 2018年2月2日 There are two main, complementary, classifications of limestone Both have advantages and disadvantages Folk’s classification (Folk 1959) describes the composition of grains and interstitial material in terms of types of grains (allochems), finegrained matrix (micrite), and crystalline cement (sparite)Grains include shell debris (bioclasts), ooids (small ovoidal Limestone SpringerLinkLIMESTONE AND OTHER CALCAREOUS MATERIALS 181 Indian Minerals Yearbook 2020 (PartIII : Mineral Reviews) 59th Edition LIMESTONE OTHER CALCAREOUS MATERIALS (ADVANCE RELEASE) GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF MINES INDIAN BUREAU OF MINES Indira Bhavan, Civil Lines, NAGPUR – 440 001LIMESTONE AND OTHER CALCAREOUS MATERIALS Indian Download scientific diagram Classification of limestones and dolomites, by calcitedolomite mineral percentage, MgO%, and stainability/colour density dispersion (graphed by using Compton [27 Classification of limestones and dolomites, by calcitedolomite
.jpg)
Representing the Dunham classification of limestone based on
Representing the Dunham classification of limestone based on depositional texture from publication: Integrated Porosity Classification and Quantification Scheme for Enhanced Carbonate Reservoir 2024年11月24日 In defining a limestone by the Folk classification the rock is named according to the nature of the material filling the spaces between the particles (ie micrite matrix or sparite cement), prefixed by an abbreviation to denote the main allochems present: bio for bioclasts, Folk limestone classification Oxford Reference2023年7月9日 Limestone is important for making cement and in construction Chalk has uses in classrooms and industries Flint was historically used for toolmaking The anthropic rock classification is a relatively new concept in the field of geology that includes rocks significantly altered or produced by human activitiesTypes of Rocks – Igneous, Sedimentary, Metamorphic2012年10月12日 Rocktype classification is a challenging and difficult job due to the heterogeneous properties of rocks In this paper, an imagebased rocktype analysis and classification method is proposed The study was conducted at a limestone mine in western India using stratified random sampling from a case study mine The analysis of collected sample Visionbased rocktype classification of limestone using multi
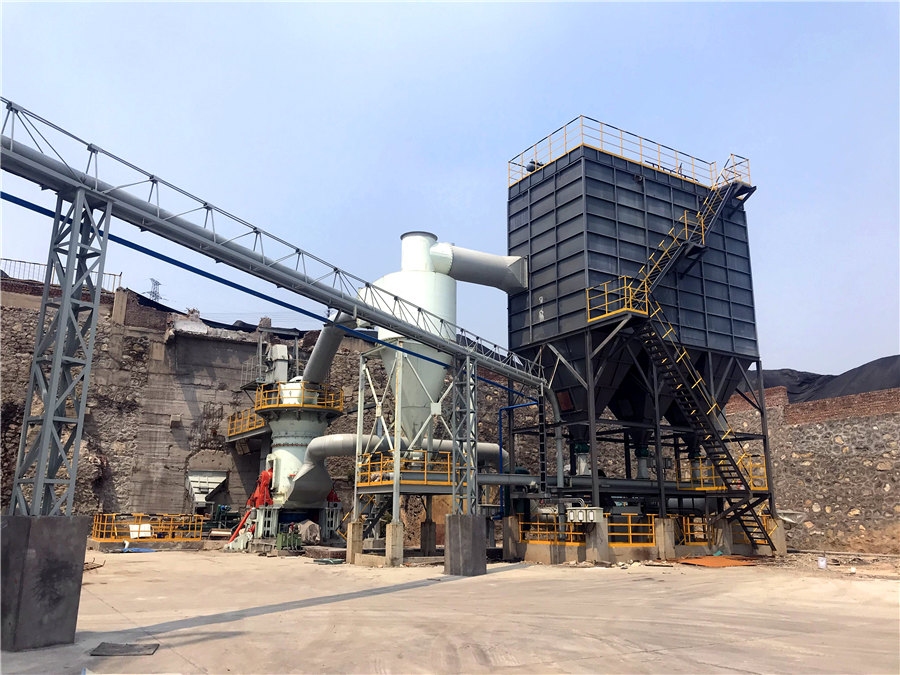

Practical petrographic classification of limestones
Recrystallization in limestone is believed to be locally abundant but of overall minor importance Among several types of recrystallization, Geological classification systems for carbonates and mudrocks were developed to more accurately describe these sedimentary rock typesBasis for the classification is (1) relative proportion of allochems and carbonate mud, (2) sorting of allochems, and (3) rounding of allochems A complete parallel exists between these limestone types and the sequence of textural maturity in sandstones, Spectral Subdivision of Limestone Types Classification of 2011年1月1日 Classification table of carbonate rocks according to Dunham's scheme[38, 43] Carbonate rocks with little or no mud content are classified as grainstones From there, the subdivisions (Figure 6 (PDF) Classification of Carbonates ResearchGateMarble is metamorphosed limestone When it forms, the calcite crystals tend to grow larger, and any sedimentary textures and fossils that might have been present are destroyed If the original limestone was pure calcite, then the 72: Classification of Metamorphic Rocks
.jpg)
List of types of limestone Wikipedia
Caen Stone – Limestone quarried near Caen, France; Lutetian limestone – Type of limestone from Paris, or "Paris stone" (city buildings are widely faced with it) SaintMaximin – commune in Oise, France, or Oise, limestone (variety of Beige Pangea Limestone Pangea Beige is a very homogeneous light brown limestone The sand, earth, and mole tones of this natural stone merge through subtle glazes producing a beige surface Applying a honed finish (matt) to the light brown limestone Pangea Beige, we obtain an aesthetic which is very similar to that of cement Types of grey Types of limestone TINO2021年6月1日 Purity classification of limestone at Madura island according to the British Geological Survey [10,15,16] Characterization and Classification of Purity of Limestone in Plant bodies are lithified to become coal When shells are cemented together they make a type of limestone So limestone can be considered chemical or organic Common Sedimentary Rocks Listed below are some common types of sedimentary rocks (Table below Sedimentary Rock Classification is shared under a CK12 license and was authored, 414: Sedimentary Rock Classification K12 LibreTexts
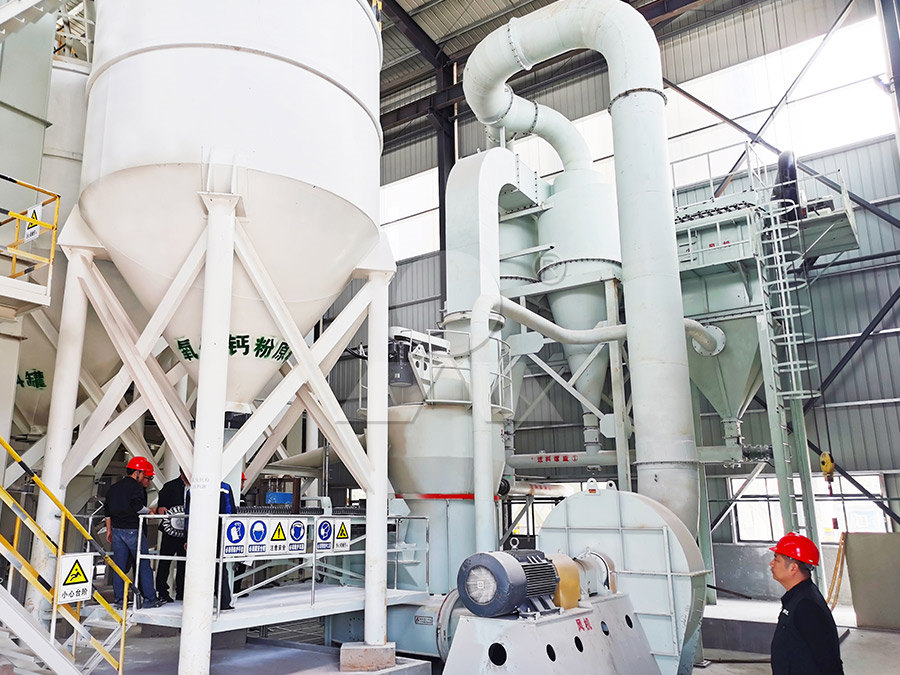

Classification of Sedimentary Rocks University of Kansas
Classification of Sedimentary Rocks by Russell B Travis Web pages adapted from Quarterly of the Colorado School of Mines, vol 50, no 1 Texture: Limestone: chiefly calcite, massive Dolomite (Dolostone): chiefly dolomite, massive Chalk: chalky texture Tufa: very porous, friableThe original Dunham classification does not subdivide limestones with particles coarser than 2 mm, or differentiate between different types of organically bound limestone These categories of limestone are defined by Embry and Clovan in their modifications to the Dunham classification See also embry and clovan classificationDunham classification Oxford ReferenceDimension limestone is divided into three sub classifications that describe their densities in approximate ranges, as follows: Low Density Limestone having a density ranging from 110 through 135 lb/ft 3 (1760 through 2160 kg/m 3) Medium DensityLimestone having a density greater than 135 and not greater than 160 lb/ft 3 (2160 through 2560 kg Geological Classification of LimestoneFolk Classification The Folk classification, which we will use in lab, is shown belowThe classification divides carbonates into two groups Allochemical rocks are those that contain grains brought in from elsewhere (ie similar to detrital grains in clastic rocks)Orthochemical rocks are those in which the carbonate crystallized in placeCarbonates Other Rocks Tulane University
.jpg)
Limestone Sedimentary rocks Sandatlas
Limestone is a very common sedimentary rock consisting of calcium carbonate (more than 50%) It is the most common nonsiliciclastic (sandstone and shale are common siliciclastic rocks) sedimentary rockLimestones are rocks that Their various sizes, from boulders to clay, is referred to as the sediment grain size The classification and description of the various clastic rocks appears in the top section of the chart below Crystalline limestone is a carbonate 55: Classification of Sedimentary Rocks Geosciences 2024年10月30日 Limestone, sedimentary rock composed mainly of calcium carbonate, usually in the form of calcite or aragonite It may contain considerable amounts of magnesium carbonate (dolomite) as well; minor constituents also Limestone Characteristics, Formation, Texture, Uses, 2019年9月4日 A post in the How to series on carbonate mineralogy – limestone classification The classification of carbonate rocks, like that of sandstones, has gone through a few iterationsTwo schemes have stood the test of trial and error, in the field and through microscopes; both were compiled in the late 1950s – early 60s, each serves a slightly different The mineralogy of carbonates; classification Geological
.jpg)
Limestone: Properties, Characteristics and Uses Geossary
The most widely used descriptive classification to define the type of limestone found in field work is that of Dunham (1962) For the classification it is necessary to base it on the texture, structural characteristics, the relationships of the primary structural components: grains (intraclasts, granules, pelloids, wrapped grains, bioclasts and skeleton), carbonate mud and calcite cementA triangular diagram showing the relative proportions of allochems, calcite ooze matrix, and sparry calcite cement is used to define three major limestone families Family I consists of abundant allochems cemented by sparry calcite; these are the cleanly washed limestones, analogous with well sorted, clayfree sandstones and similarly formed in loci of vigorous currentsPractical Petrographic Classification of Limestones1Folk limestone classification table identifies the component (or allochemical) particles and whether the matrix is micrite or lime mud or a sparry calcite cement precipitated between the grainsShould intraclasts form >25% of the grains, then the rock is named an intraclastic limestone; if intraclasts are 25%, the rock is an oolitic limestone; if intraclasts and ooids are Classification of Carbonates SpringerLinkDownload scientific diagram Folk classification of limestones based on textural parameters and implied depositional conditions from publication: Integrated Porosity Classification and Folk classification of limestones based on textural parameters and
.jpg)
A revised classification of limestones ScienceDirect
1992年3月1日 The most widely used classifications of limestones are now thirty years old and our appreciation of the diagenetic effects on limestone textures is now much greater A revision of the classifications of Dunham (1962) and Embry and Klovan (1971) is offered and new “diagenetic” categories are proposedWhat is Limestone? Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed primarily of calcite, a calcium carbonate mineral with a chemical composition of CaCO 3It usually forms in clear, calm, warm, shallow marine waters Limestone is usually a biological sedimentary rock, forming from the accumulation of shell, coral, algal, fecal, and other organic debrisLimestone: Rock Uses, Formation, Composition, Pictures