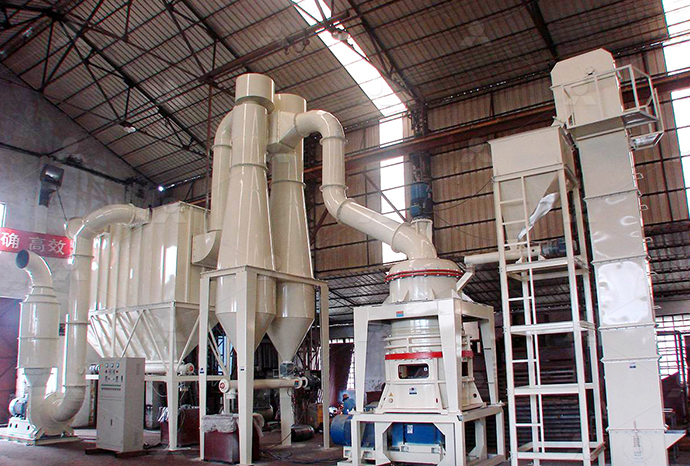
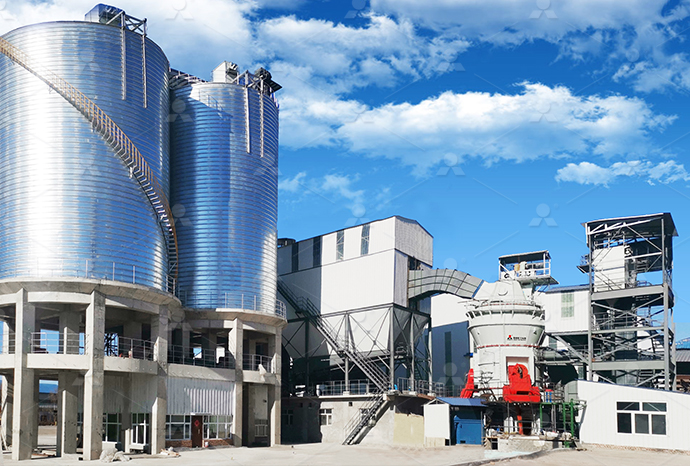
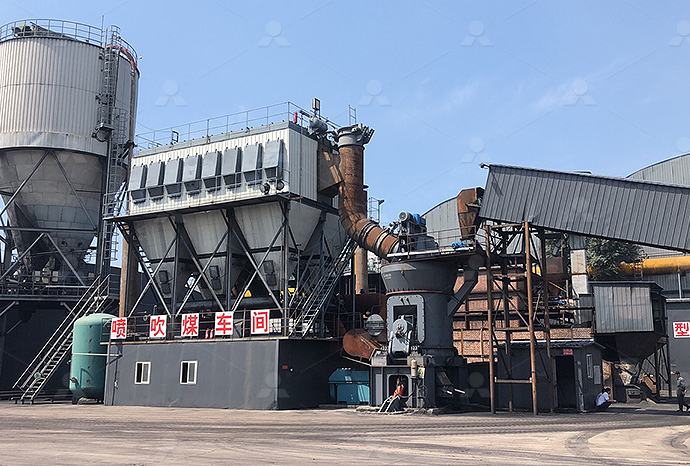
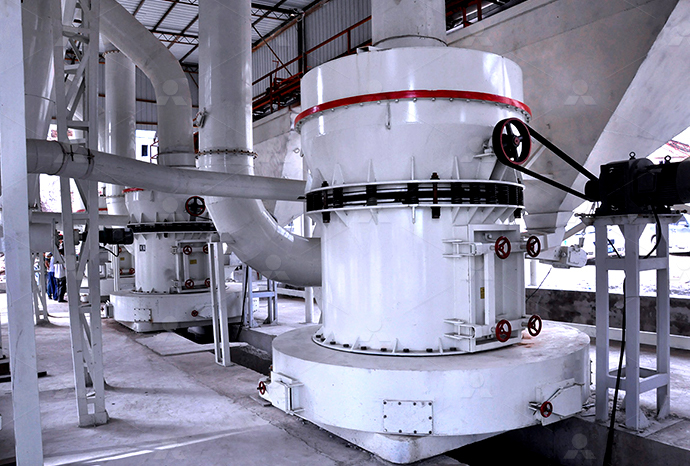
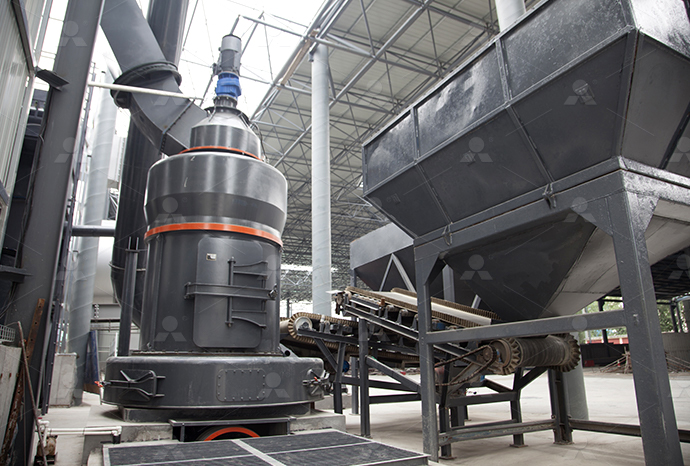
Heavy calcium carbonate limestone rock relief process
.jpg)
Karst topography: Formation, processes, characteristics, landforms
2024年1月1日 Simply put, karst refers to a unique topography that shows surface or ground water dissolving (also known as chemically settling) soluble rocks beneath Karst terrain can be formed by highly soluble rocks like gypsum and rock salt, despite their usual association with 2024年5月16日 The current experimental work aimed at developing PCC through two major process steps: dissolution and precipitation, using raw materials domestically available as SL, Evaluation of precipitated CaCO3 produced from locally available 2005年11月1日 Any MgCO 3 present in the limestone will act as inert MgO during the CO 2 sequestration process The addition of limestone at a high temperature to a contacting vessel Review—calcination and carbonation of limestone during thermal 2023年11月1日 Ignoring the buffering effect of carbonate rocks on the heavy metals in the mine environment leads to inaccurate ecological risk assessment, wasting land resources and Carbonate rocks as natural buffers: Exploring their environmental
.jpg)
Limestone Quarrying and Processing: A LifeCycle Inventory
Chemical limestone forms when calcium and carbonate ions suspended in water chemically bond and precipitate from their aquatic sources Because of its high calcium content, limestone is 2021年7月22日 Our results indicate that the subduction and diapirism of limestone is potentially a key process for the transport and storage of sedimentary carbonate in the deep crust and the lithosphereMassive carbon storage in convergent margins 2022年4月12日 Calcium carbonate extracted from chalk or limestone is used as an agricultural fertilizer in slightly acidic soils and in the treatment of drinking water Calcium oxide (lime) is Calcium Carbonate (Calcite) SpringerLink2022年9月19日 In this study, the rainfall/throughfall, runoff from exposed limestone, and corresponding changes in the Ca 2+ concentration of forested and cleared plots were Raininduced weathering dissolution of limestone and
.jpg)
How Limestone is Formed, Where Does it Form? –
Factors Influencing Location Several factors influence where limestone forms: Presence of Calcium Carbonate Source: Readily available dissolved calcium carbonate, either from seawater, freshwater, or weathering of carbonate 2016年10月13日 This procedure includes general information on the characteristics and common uses of limestone and identifies typical problems associated with the material See also 0440001S for guidance on inspecting stone masonry failuresIntroductionLimestone is a sedimentary rock composed principally of calcium carbonate (calcite) or the double carbonate Limestone: Characteristics, Uses And Problem GSA21 Limestone Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed primarily of calcium carbonate with the occasional presence of magnesium Most limestone is biochemical in origin meaning the calcium carbonate in the stone originated from shelled oceanic creatures Limestone can also be chemical in origin as is the case with travertineLimestone Quarrying and Processing: A LifeCycle Inventory2024年10月30日 Limestone, sedimentary rock composed mainly of calcium carbonate, usually in the form of calcite or aragonite It may contain considerable amounts of magnesium carbonate (dolomite) as well; minor constituents also commonly present include clay, iron carbonate, feldspar, pyrite, and quartzLimestone Characteristics, Formation, Texture, Uses, Facts
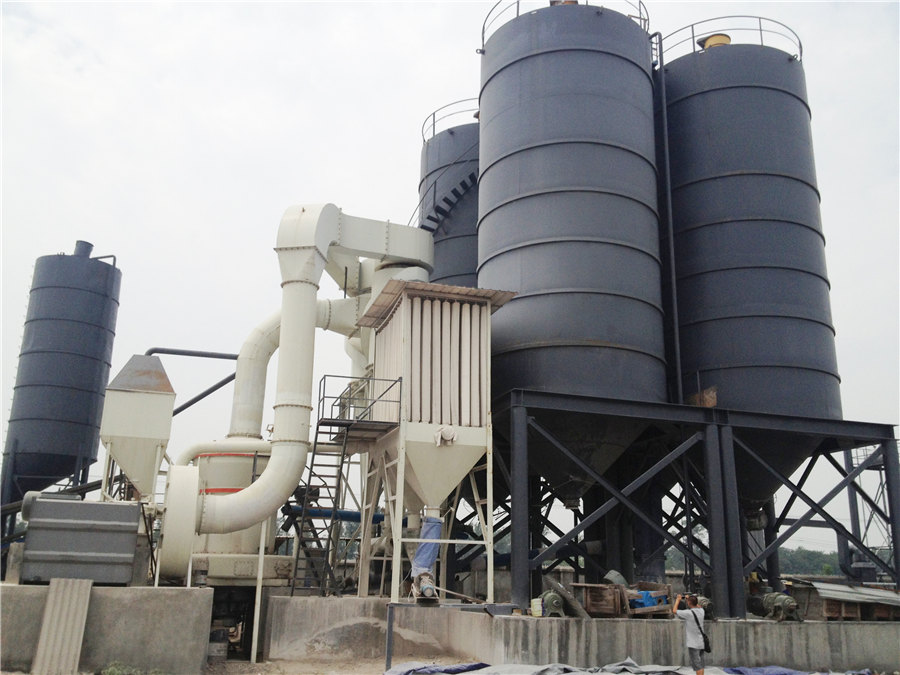

Limestone Formation, Composition, Types and Uses Earth Eclipse
Limestone, or calcium carbonate, is the common rock found throughout the world Oldest and perhaps slightly overlooked, limestone is very much part of our everyday life It may be hidden with your walls, in the water you drink, the food you consume, or in the cosmetics2017年1月1日 PDF Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is the most widely used filler material in paper, paint, plastic, food, ceramic, cosmetic, medicine and other Find, read and cite all the research you need on Precipitated Calcium carbonate production, synthesis and propertiesLimestone is an unusual rock in that it fizzes when dilute acid is placed on its surface It is the presence of calcium carbonate that is responsible for this The calcium carbonate content of limestone rocks has been used from the earliest civilisations, dating back to 14,000 BCE, to its extensive use in modern timesLimestone, a fizzy rock – introduction Science Learning Hub2022年4月12日 Limestone is a sedimentary rock comprised chiefly of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) Deposits are extensive around the world Therefore, there is a high variability of limestone deposits Typically, they are formed in two main environmentsCalcium Carbonate (Calcite) SpringerLink
.jpg)
(PDF) Environmental Hazards of Limestone Mining and
2020年2月18日 Limestone is a fundamental raw material in various industrial sectors It is formed due to biochemical precipitation of calcium carbonate, and further compaction over long periods of time2013年9月1日 The scope of the investigations was to determine the quantity of total (Cu, Zn and Pb) and available forms of heavy metals (Cu, Fe, Mn and Zn) in soils formed on limestone and dolomite on the (PDF) Content of heavy metals in soils formed on limestone and Related pages Limestone – Limestone is a carbonate sedimentary rock that consists predominantly of calcite [CaCO3] Limestones are the commonest rocks that contain nonsilicate minerals as primary components and, even if they Carbonate Rocks Geology is the Way2017年3月9日 The current high global demand for highquality paper, paint, adhesive/sealant, and plastic, filler industries cannot survive without unique and highquality precipitated calcium carbonate (PCC) They are used as fillers, additives, and reinforcements PCC is a key constituent of the modern paper and plastic industry This article reports the effect of various Synthesis of precipitated calcium carbonate: a review
.jpg)
Limestone Geology is the Way
Limestone is a carbonate sedimentary rock that consists predominantly of calcite [CaCO 3]Limestones are the commonest rocks that contain nonsilicate minerals as primary components and, even if they represent only a fraction of all It starts off as sediment, and it must have more than 50% calcium carbonate in it to qualify as limestone Rock such as mudstone or sandstone – where the grains have come down rivers and been delivered to the sea – they can have a highish calcium carbonate content perhaps as well, but less than 50%, and so we could call those calcareous Limestone secrets revealed — Science Learning Hub2024年10月6日 Weathering is the breakdown of rock by physical, chemical or biological processes Limestone areas are predominantly affected by chemical weathering when rainwater, which contains a weak carbonic acid, reacts with limestone This causes the limestone to dissolve Carbon dioxide from the respiration of animals (and ourselves) is one cause of How does weathering affect limestone? Internet Geography2023年12月26日 Chemical Properties of CaCO 3 The chemical properties of calcium carbonate can be visualized in terms of chemical reaction it undergoes Let's have glance on the chemical reactions of CaCO 3 Reaction of CaCO 3 with Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) Calcium Carbonate on reacting with HCl gives calcium chloride salt and carbon dioxide gas which causes effervesenceCalcium Carbonate(CaCO3) Limestone Formula, Structure, Uses
.jpg)
Unlocking the Potential of High Calcium Limestone: Soil
2023年5月3日 High Calcium Limestone High calcium limestone is a type of limestone that is composed mainly of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), with a calcium carbonate equivalent (CCE) of at least 90% High calcium limestone is an important source of agricultural lime, which is used to improve soil fertility and pH balanceAs marble, calcium carbonate is a coarsecrystalline, metamorphic rock, which is formed when chalk or limestone is recrystallized under conditions of high temperature and pressure Large deposits of marble are found in North America and in Europe; eg, in Carrara, Italy, the home of the pure white "statuario" from which Michelangelo created his sculpturesWhat is Calcium Carbonate? SHC Group Vietnam SHC Among the sedimentary rocks we find socalled biochemical rocks such as carbonates of calcium (limestone), phosphates of calcium (fluoro, chloro and hydroxapatite) and Carbonic acid contained in snow or rainwater slowly erodes the rock, dissolving the limestone (Box 2, reactions 1 and 2) generating characteristic reliefs Limestone and calcium in plants Soin de la TerreLimestone and marble Chemically, limestone is calcium carbonate It is a sedimentary rock formed from the shells and skeletons of marine creatures which fell to the bottom of ancient seas These were turned into rock by the pressure of more sediments forming on top of themlimestone, quicklime and slaked lime chemguide
.jpg)
Limestone Sedimentary rocks Sandatlas
Limestone is a very common sedimentary rock consisting of calcium carbonate (more than 50%) It is the most common nonsiliciclastic (sandstone and shale are common siliciclastic rocks) sedimentary rockLimestones are rocks that 2023年11月21日 Limestone can be formed in a few different ways Because limestone's main characteristic is that it is a sedimentary rock made of calcium carbonate, there are a few possibilities for the formation Limestone Definition, Types Uses Lesson2017年1月1日 The calcium looping CO2 capture process using calcium oxide as a regenerable solid sorbent has been under development at the Industrial Technology Research Institute (ITRI) of Taiwan for several Calcium Carbonate Looping: CO2 capture by using limestone in Calcium carbonate is only readily soluble in pure water if the water is acidic As the carbon dioxide level of the water decreases, the acidity will also decrease along with the solubility of calcium carbonate In drier caves evaporation might also play a role leaving behind deposits of calcium carbonate in the form of calcite or aragonite124: Karst Cave Features, Cave Contents, and Subterranean Life
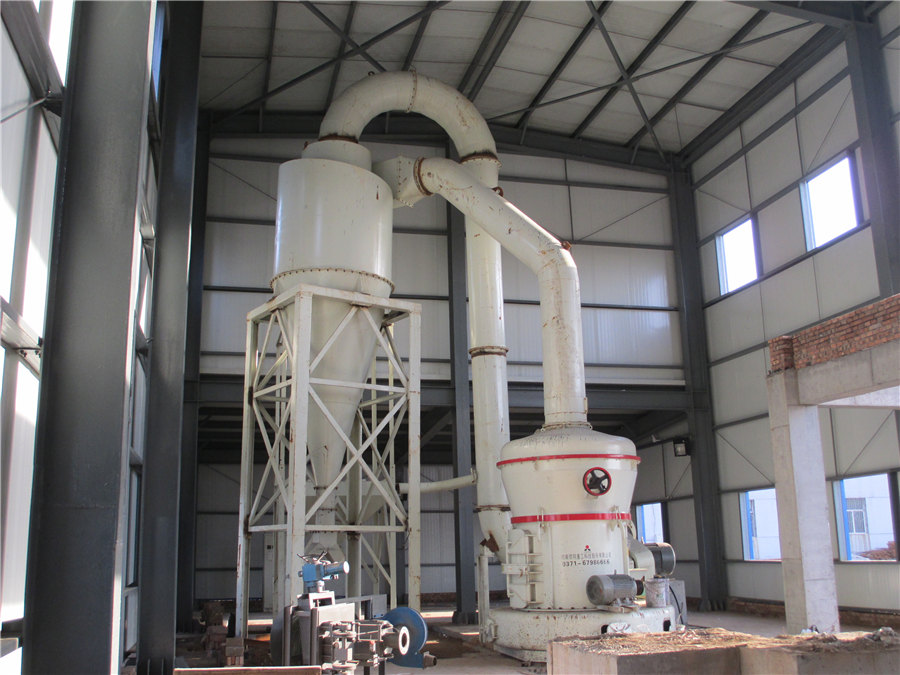

Limestone Water Filter (Ultimate Guide) Aquahow
2022年4月19日 Carbon dioxide (CO2) bubbles are formed when calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is added to water Calcium ions (Ca2+) combine with carbonate ions (CO32) in limestone to form calcium carbonate (CaCo3) Because there are more hydroxide ions than hydrogen ions in the solution, the pH should be higher than 7, indicating that the solution is essential2010年2月2日 Calcium Carbonate MMH Al Omari, AA Badwan, in Profiles of Drug Substances, Excipients and Related Methodology, 2016 21 Existence in Nature CaCO 3 is one of the most abundant materials found in earth's crust and forms the rock types like limestone and chalk [10]Moreover, it is the most abundant chemical sediment in modern and most ancient Carbonate Rock an overview ScienceDirect Topics2023年11月1日 The main mechanism of carbonate buffering delays the migration of heavy metals released from AMD in two main ways: (1) releasing CO 3 2− and HCO 3 − from the dissolution of carbonate rocks depletes large amounts of acid produced by AMD, which promotes the adsorption and coprecipitation of heavy metals by secondary minerals and organic Carbonate rocks as natural buffers: Exploring their environmental 2017年8月16日 In 1993, published research derived from 1985 drilling on the edge of the Blake Plateau of the Grand Banks in the Bahamas showed that the Mesozoic carbonate gigabank had already existed in the late Jurassic and early Cretaceous periods, approximately 125 million years agoThe Blake Plateau lies between the continental shelf and the deep ocean basin that runs THE LIMESTONE ROCK OF THE BAHAMAS Bahamianology
.jpg)
Limestone: characteristics, formation, uses ZME Science
2024年1月7日 Limestone is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock primarily composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) It typically comprises two different minerals: calcite and aragonite, which have the same Particle Morphology Controlling Technique Calcium carbonate has three crystalline polymorphs: calcite, aragonite, and vaterite In the carbonation process, these crystals can be produced by changing various conditions such as concentration and temperature of lime milk, introduction rate of CO 2 gas, and whether or not chemicals are added All reaction formulas are expressed as How Calcium Carbonate is Produced?|Manufacturing|COREFactors Influencing Location Several factors influence where limestone forms: Presence of Calcium Carbonate Source: Readily available dissolved calcium carbonate, either from seawater, freshwater, or weathering of carbonate How Limestone is Formed, Where Does it Form? – 2016年10月13日 This procedure includes general information on the characteristics and common uses of limestone and identifies typical problems associated with the material See also 0440001S for guidance on inspecting stone masonry failuresIntroductionLimestone is a sedimentary rock composed principally of calcium carbonate (calcite) or the double carbonate Limestone: Characteristics, Uses And Problem GSA
.jpg)
Limestone Quarrying and Processing: A LifeCycle Inventory
21 Limestone Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed primarily of calcium carbonate with the occasional presence of magnesium Most limestone is biochemical in origin meaning the calcium carbonate in the stone originated from shelled oceanic creatures Limestone can also be chemical in origin as is the case with travertine2024年10月30日 Limestone, sedimentary rock composed mainly of calcium carbonate, usually in the form of calcite or aragonite It may contain considerable amounts of magnesium carbonate (dolomite) as well; minor constituents also commonly present include clay, iron carbonate, feldspar, pyrite, and quartzLimestone Characteristics, Formation, Texture, Uses, FactsLimestone, or calcium carbonate, is the common rock found throughout the world Oldest and perhaps slightly overlooked, limestone is very much part of our everyday life It may be hidden with your walls, in the water you drink, the food you consume, or in the cosmeticsLimestone Formation, Composition, Types and Uses Earth Eclipse2017年1月1日 PDF Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is the most widely used filler material in paper, paint, plastic, food, ceramic, cosmetic, medicine and other Find, read and cite all the research you need on Precipitated Calcium carbonate production, synthesis and properties
.jpg)
Limestone, a fizzy rock – introduction Science Learning Hub
Limestone is an unusual rock in that it fizzes when dilute acid is placed on its surface It is the presence of calcium carbonate that is responsible for this The calcium carbonate content of limestone rocks has been used from the earliest civilisations, dating back to 14,000 BCE, to its extensive use in modern times2022年4月12日 Limestone is a sedimentary rock comprised chiefly of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) Deposits are extensive around the world Therefore, there is a high variability of limestone deposits Typically, they are formed in two main environmentsCalcium Carbonate (Calcite) SpringerLink2020年2月18日 Limestone is a fundamental raw material in various industrial sectors It is formed due to biochemical precipitation of calcium carbonate, and further compaction over long periods of time(PDF) Environmental Hazards of Limestone Mining and2013年9月1日 The scope of the investigations was to determine the quantity of total (Cu, Zn and Pb) and available forms of heavy metals (Cu, Fe, Mn and Zn) in soils formed on limestone and dolomite on the (PDF) Content of heavy metals in soils formed on limestone and